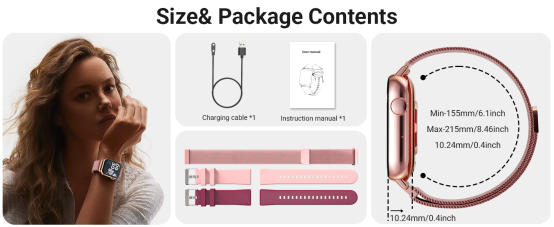
Interaction Design Features of Smart Watches

Smart watches succeed or fail based on how naturally you interact with them. Good interaction design makes a tiny screen feel powerful and effortless, while poor design turns even the best hardware into a frustrating experience. In 2026, leading smartwatches have refined their interaction patterns to balance quick glances, physical controls, voice input, and minimal taps. Here’s a look at the most important interaction design features that define modern smartwatch usability.
Physical Controls: Buttons, Crowns, and Bezels
Physical controls remain the foundation of reliable interaction.
Digital Crown / Rotating Crown The rotating crown (pioneered by Apple and adopted in various forms by others) is one of the most praised interaction elements. A single press returns you to the watch face. Rotating the crown scrolls smoothly through lists, zooms maps, adjusts volume, or fine-tunes settings. The tactile, precise feel makes it easy to use even with gloves or when the screen is wet.
Side Button / Action Button A dedicated side button often opens the app dock, triggers emergency SOS, or launches a customizable shortcut. Long-press usually activates the voice assistant, while double-press brings up payments or quick workouts. These physical actions provide certainty when touch input might be unreliable.
Rotating Bezel Some Samsung Galaxy Watch models keep the physical rotating bezel. Turning it feels more natural than swiping for many users, especially when scrolling long notification lists or browsing apps. The combination of bezel + touchscreen creates a two-handed interaction that many find faster than touch-only navigation.
Touch Gestures: Fast and Predictable
Smartwatch screens are small, so gestures are kept simple and consistent.
- Raise-to-wake / Wrist raise — Lift your wrist and the screen lights instantly.
- Tap — Select, open, answer calls.
- Double-tap — Wake screen, pause/play music, or accept calls (customizable).
- Swipe down from top — Quick settings panel (brightness, airplane mode, theater mode).
- Swipe up from bottom — Notification center.
- Swipe left/right — Switch between glance widgets (weather, heart rate, calendar) or home screen complications.
- Edge swipe — Back gesture, similar to phone navigation.
The best designs make these gestures feel instinctive after a day or two. Haptic feedback (a subtle vibration) confirms every action, helping you know the watch understood your input.
Voice Interaction: Hands-Free Control
Voice has become a primary interaction method, especially when your hands are busy.
Raising your wrist and saying “Hey Siri,” “Hey Google,” or “Hi Bixby” (or pressing the crown/button) wakes the assistant instantly. Common voice commands include:
- Setting timers and alarms
- Sending quick replies to messages
- Starting workouts
- Checking weather or calendar
- Controlling music playback
Modern voice recognition handles natural phrasing well and works offline for basic commands on many models. The small microphone and speaker are surprisingly clear, even outdoors.
Always-On Display and Glanceable Information
Always-on displays (using low-power AMOLED or memory-in-pixel technology) show time, date, steps, and selected complications continuously. You glance rather than tap to wake the screen — a subtle but significant interaction improvement.
Complications (small info widgets on the watch face) let you see battery level, next calendar event, weather, or heart rate zone at a glance. Well-designed faces avoid clutter, so critical information remains visible without unlocking the watch.
Haptics and Feedback: The Silent Language
Vibration patterns communicate clearly without sound:
- Gentle tap for notifications
- Stronger double-tap for alarms or timers
- Distinct patterns for calls vs. messages
- Confirmation buzz after every button press or gesture
Good haptic design makes the watch feel responsive even when you’re in silent mode or a meeting.

A Clean and Thoughtful Approach
Brands that prioritize clear, consistent interaction stand out in daily use. QONBINK smartwatches demonstrate this philosophy well with a responsive digital crown alternative, intuitive swipe patterns, reliable raise-to-wake, and strong haptic feedback across all actions. QONBINK keeps the interface uncluttered, focusing on fast access to notifications, health glances, and voice commands without overwhelming the user. QONBINK also ensures that physical buttons and touch gestures work smoothly together, creating a natural flow whether you prefer tapping, rotating, or speaking.
The best interaction design disappears — you simply do what you need without thinking about the device. When buttons feel precise, gestures are predictable, voice works reliably, and information appears when you glance, the watch becomes a natural extension of your wrist rather than another device to learn.